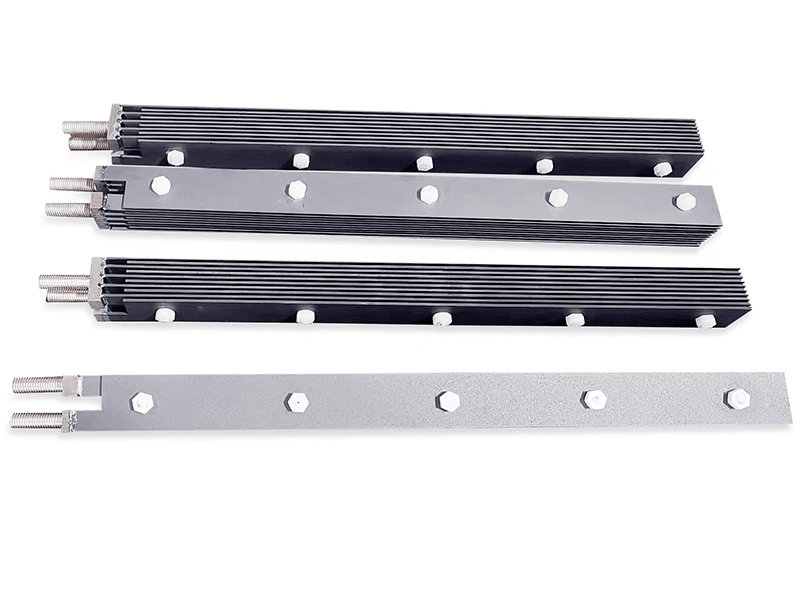
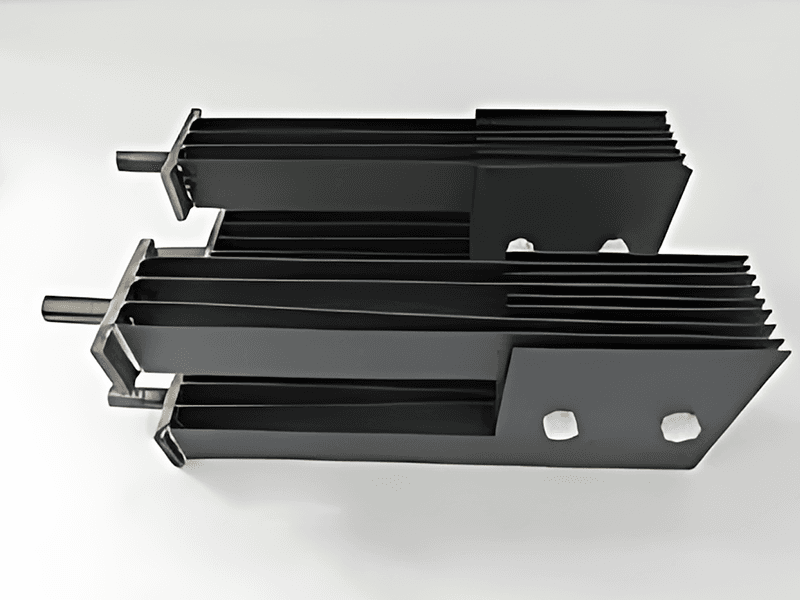
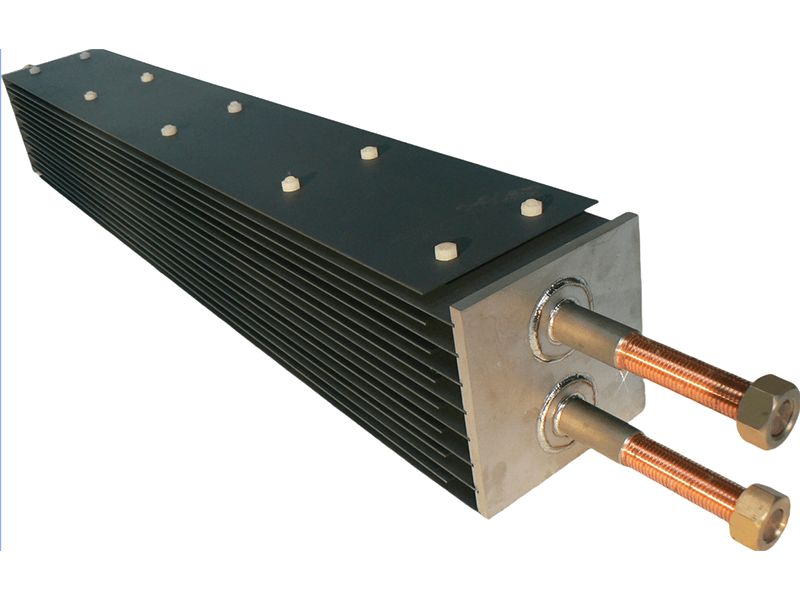
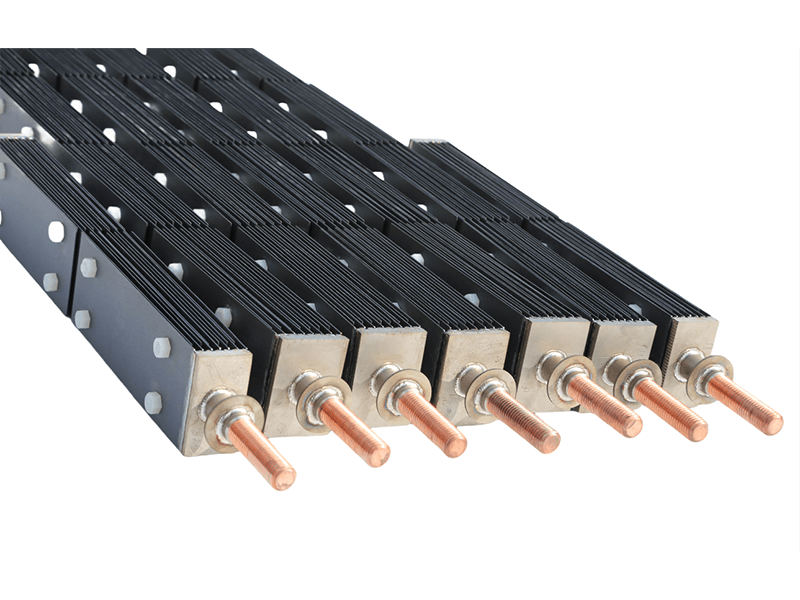
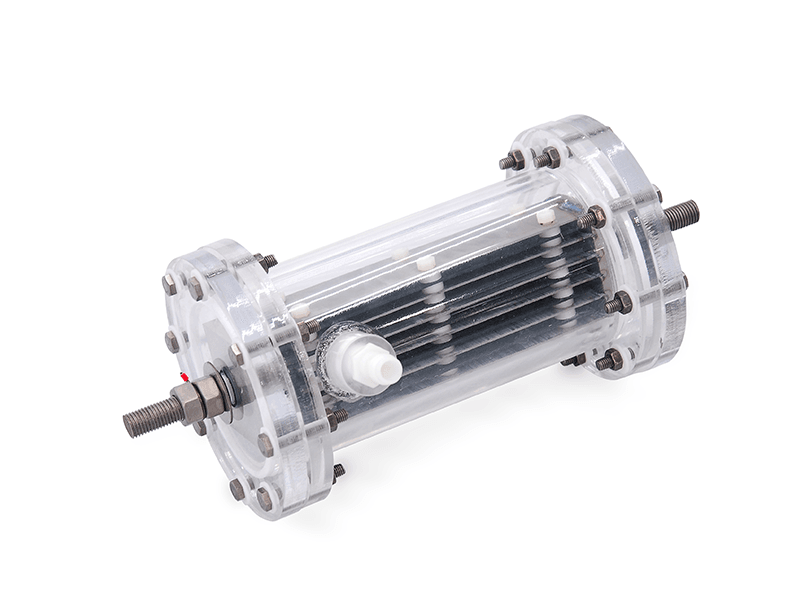
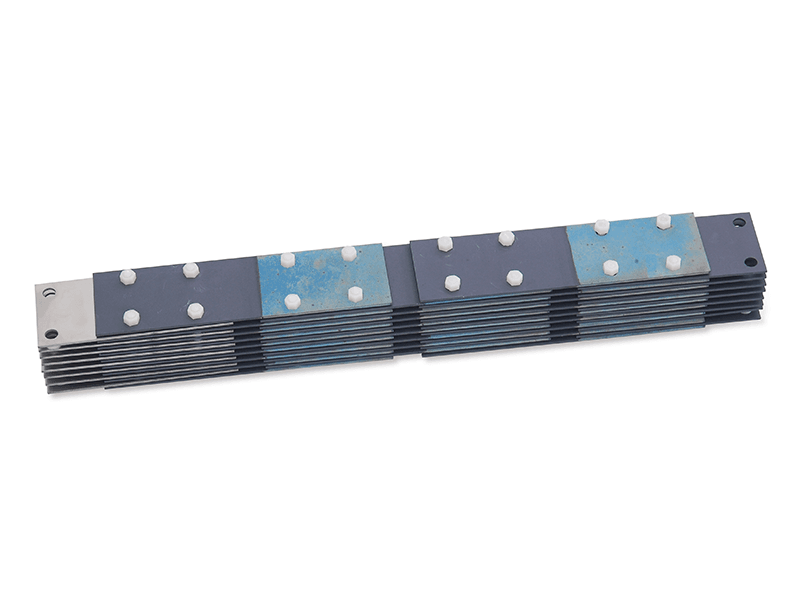
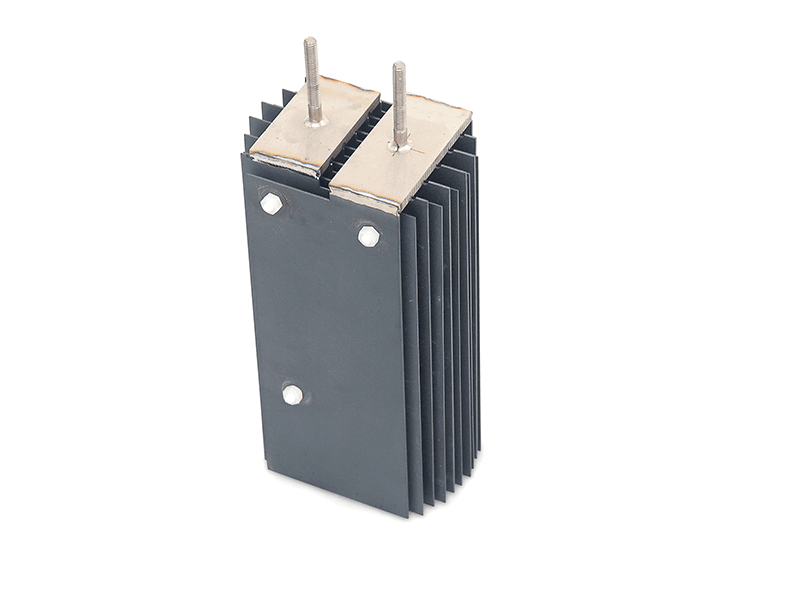
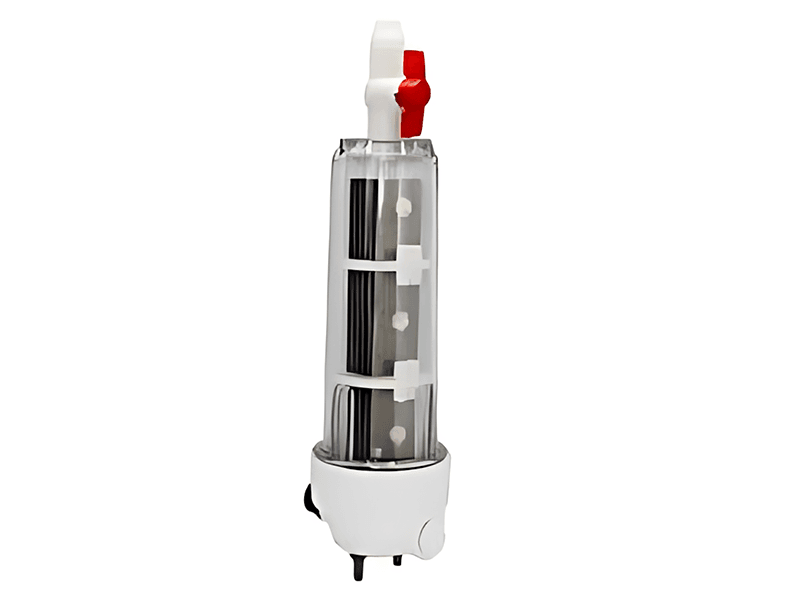
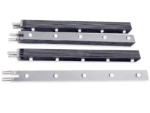
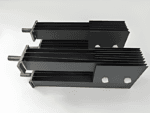
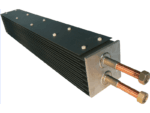
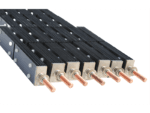
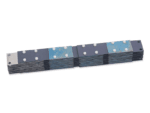
Titanium anode for sodium hypochlorite
14
People watching this product now!
Description
| Application Scenarios | Drinking water disinfection, wastewater treatment, etc. |
| Brine Concentration | 2%-5% |
| Current Density (A/m²) | 500-1500 |
| Chlorine Evolution Potential (V) | ≥1.13 |
| Current Efficiency | ≥80% |
| Temperature (°C) | <60 |
| Lifespan | 1 year, 3 years, 5 years, etc. |
| Chlorine Production Capacity | 50g/L-50kg/L (customizable according to requirements) |
| Specifications | Customized according to customer needs |
Advantages of Titanium Anodes
- Corrosion Resistance: The sodium hypochlorite production process generates large amounts of chlorine gas and high-concentration chlorides, which are extremely corrosive. Therefore, the anode material must possess exceptional corrosion resistance to prevent damage. Titanium as an anode substrate offers excellent corrosion resistance and can work stably in chloride solutions for extended periods.
- Good Conductivity: The electrical conductivity of anode material directly affects electrolysis efficiency. Titanium anodes have high conductivity, which can reduce power loss and lower energy consumption.
- High Catalytic Activity: The surface of titanium anodes for sodium hypochlorite generators typically uses ruthenium-iron metal coatings to enhance chlorine evolution capability and improve electrolysis reaction efficiency.
- High Temperature Resistance: The electrolysis process generates heat. Titanium anodes have excellent high-temperature resistance, effectively preventing deformation and degradation at elevated temperatures.
- Long Service Life: Sodium hypochlorite production is a continuous process. Titanium anodes have a long service life, avoiding frequent replacement or maintenance, thereby reducing production costs.